E2E UI Test Generator
Streamline the process of creating and maintaining comprehensive end-to-end tests for web applications using the Playwright testing framework.
Generate robust and maintainable test scripts that can be seamlessly integrated into a CI/CD pipeline.
Key Features
-
Test Plan Generation: The feature analyzes the application requirements or specifications and automatically generates a comprehensive test plan, covering various user flows and scenarios.
-
Playwright Test Script Generation: Based on the test plan, the feature generates Playwright test scripts written in Python 3.9, following best practices and industry standards.
-
Page Object Model: The generated scripts implement the Page Object Model (POM) design pattern, promoting code reusability, maintainability, and separation of concerns.
-
Web Element Interaction: The scripts leverage Playwright's powerful features for interacting with web elements, such as clicking buttons, filling out forms, and navigating between pages.
-
Visual Testing: The feature utilizes Playwright's capabilities to capture screenshots and videos during test execution, enabling visual validation and debugging.
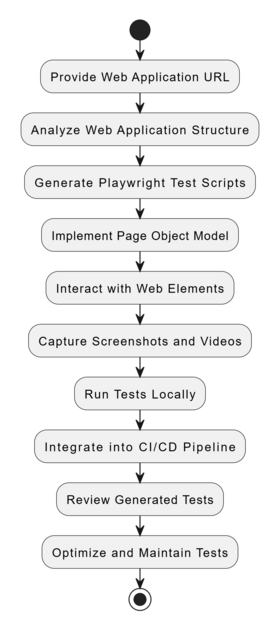
How it Works
- Provide the URL of the web application you want to test.
- The E2E UI Test Generator analyzes the web application's content and structure.
- It generates comprehensive Playwright test scripts covering various UI modules and user flows.
- The generated scripts can be executed locally or integrated into a CI/CD pipeline.
You can find an example here (opens in a new tab)
Usage Guide
Here's a detailed step-by-step guide on how to use the E2E UI Test Generator:
-
Follow the initial setup guide here.
-
Create a new Python file and import the E2ETestGenerator module:
from kaizen.generator.e2e_tests import E2ETestGenerator -
Create an instance of the E2ETestGenerator:
generator = E2ETestGenerator() -
Generate E2E tests for a specific URL:
WEBPAGE_URL = "https://example.com" tests, * = generator.generate_e2e_tests(WEBPAGE_URL) -
Display the generated tests:
for test in tests: print(f'Module Title: {test["module_title"]} || Importance: {test["importance"]}') for t in test["tests"]: print(f'Description: {t["test_description"]}') print(f'Code: \n{t["code"]}') print("-----------------------------------------------------------") -
Run the generated tests:
results = generator.run_tests() print(f"Test Execution results: \n {results}") -
Review the generated tests and execution results, and integrate them into your development workflow.
Example
Here's a complete example to generate and run E2E UI tests:
from kaizen.generator.e2e_tests import E2ETestGenerator
import time
import sys
import traceback
# Create an instance of the E2E Test Generator
generator = E2ETestGenerator()
# Set the webpage URL to test
WEBPAGE_URL = "https://cloudcode.ai"
print(f"Generating UI tests for `{WEBPAGE_URL}`, please wait...")
start_time = time.time()
try:
# Generate E2E tests
tests, * = generator.generate_e2e_tests(WEBPAGE_URL)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
print(traceback.format_exc())
sys.exit(1)
end_time = time.time()
elapsed_time = end_time - start_time
print(f"\nUI tests generated in {elapsed_time:.2f} seconds.")
# Display generated tests
for test in tests:
print(
f'#### ======== Module Title: {test["module_title"]} || Importance: {test["importance"]} ========== ####'
)
for t in test["tests"]:
print(f'Desc: {t["test_description"]}')
print(f'Code: \n{t["code"]}')
print("-----------------------------------------------------------")
# Run the generated tests
results = generator.run_tests()
print(f"Test Execution results: \n {results}")To execute the generated tests:
import pytest
if __name__ == "__main__":
test_dir = ".kaizen/tests"
pytest.main(
[
"--timeout=60",
"-v",
test_dir,
]
)Supported Frameworks
- Playwright
Benefits
- Accelerated Test Development
- Improved Test Coverage
- Maintainability and Reusability
- Continuous Quality Assurance
- Visual Validation
- Scalability
Limitations
- Dynamic Content: May have limitations with highly dynamic or JavaScript-heavy applications.
- Complex Interactions: Advanced user interactions might require manual scripting.
- Test Data Management: Might need additional setup for managing test data across different environments.